|
Plasticity (physics), Plasticity
Plasticity may refer to: Science * Plasticity (physics), in engineering and physics, the propensity of a solid material to undergo permanent deformation under load * Behavioral plasticity, change in an organism's behavior in response to exposure to stimuli * Neuroplasticity, in neuroscience, how entire brain structures, and the brain itself, can change as a result of experience ** Synaptic plasticity, the property of a neuron or synapse to change its internal parameters in response to its history ** Metaplasticity, the plasticity of synapses * Phenotypic plasticity, in biology, describes the ability of an organism to change its phenotype in response to changes in the environment Art and entertainment * Plastic arts, such as clay sculpture, in which material is formed or deformed into a new, permanent shape * ''Plasticity'', an album by Cabaret Voltaire * ''Plasticity'', a non-album single from Front Line Assembly released alongside '' Hard Wired'' * "Plasticities", a song by And ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasticity (physics)
In physics and materials science, plasticity (also known as plastic deformation) is the ability of a solid material to undergo permanent Deformation (engineering), deformation, a non-reversible change of shape in response to applied forces. For example, a solid piece of metal being bent or pounded into a new shape displays plasticity as permanent changes occur within the material itself. In engineering, the transition from Elasticity (physics), elastic behavior to plastic behavior is known as Yield (engineering), yielding. Plastic deformation is observed in most materials, particularly metals, soils, Rock (geology), rocks, concrete, and foams. However, the physical mechanisms that cause plastic deformation can vary widely. At a crystalline scale, plasticity in metals is usually a consequence of dislocations. Such defects are relatively rare in most crystalline materials, but are numerous in some and part of their crystal structure; in such cases, plastic crystallinity can resul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Behavioral Plasticity
Behavioral plasticity is the change in an organism's behavior that results from exposure to stimuli, such as changing environmental conditions. Behavior can change more rapidly in response to changes in internal or external stimuli than is the case for most morphological traits and many physiological traits. As a result, when organisms are confronted by new conditions, behavioral changes often occur in advance of physiological or morphological changes. For instance, larval amphibians changed their antipredator behavior within an hour after a change in cues from predators, but morphological changes in body and tail shape in response to the same cues required a week to complete. Background For many years, ethologists have studied the ways that behavior can change in response to changes in external stimuli or changes in the internal state of an organism. In a parallel literature, psychologists studying learning and cognition have spent years documenting the many ways that experiences ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuroplasticity
Neuroplasticity, also known as neural plasticity or just plasticity, is the ability of neural networks in the brain to change through neurogenesis, growth and reorganization. Neuroplasticity refers to the brain's ability to reorganize and rewire its neural connections, enabling it to adapt and function in ways that differ from its prior state. This process can occur in response to learning new skills, experiencing environmental changes, recovering from injuries, or adapting to sensory or cognitive deficits. Such adaptability highlights the dynamic and ever-evolving nature of the brain, even into adulthood. These changes range from individual neuron pathways making new connections, to systematic adjustments like cortical remapping or neural oscillation. Other forms of neuroplasticity include homologous area adaptation, cross modal reassignment, map expansion, and compensatory masquerade. Examples of neuroplasticity include neural circuit, circuit and network changes that result fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
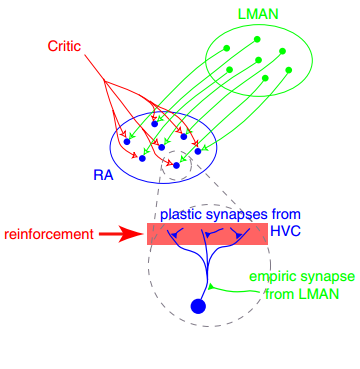
Synaptic Plasticity
In neuroscience, synaptic plasticity is the ability of synapses to Chemical synapse#Synaptic strength, strengthen or weaken over time, in response to increases or decreases in their activity. Since memory, memories are postulated to be represented by vastly interconnected neural circuits in the brain, synaptic plasticity is one of the important neurochemical foundations of learning and memory (''see Hebbian theory''). Plastic change often results from the alteration of the number of neurotransmitter receptors located on a synapse. There are several underlying mechanisms that cooperate to achieve synaptic plasticity, including changes in the quantity of neurotransmitters released into a synapse and changes in how effectively cells respond to those neurotransmitters. Synaptic plasticity in both Excitatory synapse, excitatory and Inhibitory synapse, inhibitory synapses has been found to be dependent upon postsynaptic calcium release. Historical discoveries In 1973, Terje Lømo and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metaplasticity
Metaplasticity is a term originally coined by W.C. Abraham and M.F. Bear to refer to the plasticity of synaptic plasticity. Until that time synaptic plasticity had referred to the plastic nature of ''individual'' synapses. However this new form referred to the plasticity of the plasticity itself, thus the term ''meta''-plasticity. The idea is that the synapse's previous history of activity determines its current plasticity. This may play a role in some of the underlying mechanisms thought to be important in memory and learning such as long-term potentiation (LTP), long-term depression (LTD) and so forth. These mechanisms depend on current synaptic "state", as set by ongoing extrinsic influences such as the level of synaptic inhibition, the activity of modulatory afferents such as catecholamines, and the pool of hormones affecting the synapses under study. Recently, it has become clear that the prior history of synaptic activity is an additional variable that influences the synaptic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
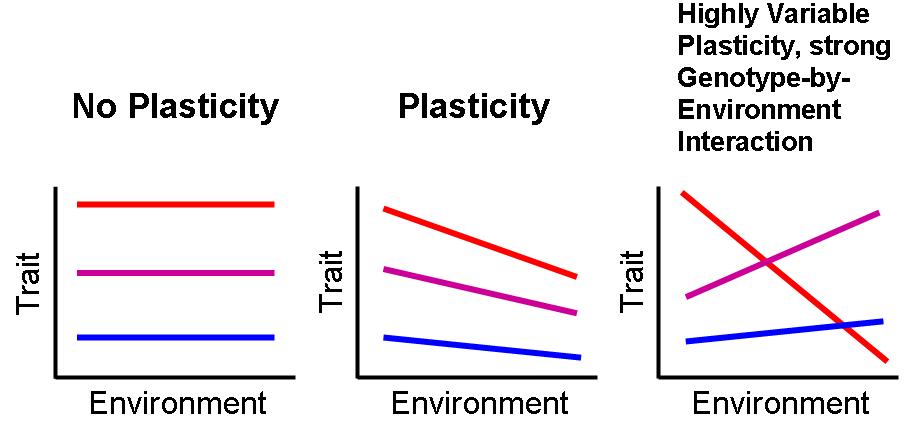
Phenotypic Plasticity
Phenotypic plasticity refers to some of the changes in an organism's behavior, morphology and physiology in response to a unique environment. Fundamental to the way in which organisms cope with environmental variation, phenotypic plasticity encompasses all types of environmentally induced changes (e.g. morphological, physiological, behavioural, phenological) that may or may not be permanent throughout an individual's lifespan. The term was originally used to describe developmental effects on morphological characters, but is now more broadly used to describe all phenotypic responses to environmental change, such as acclimation (acclimatization), as well as learning. The special case when differences in environment induce discrete phenotypes is termed polyphenism. Generally, phenotypic plasticity is more important for immobile organisms (e.g. plants) than mobile organisms (e.g. most animals), as mobile organisms can often move away from unfavourable environments. Nevertheless ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plastic Arts
Plastic arts are art forms which involve physical manipulation of a ''plastic medium'', such as clay, wax, paint or even plastic in the modern sense of the word (a ductile polymer) to create works of art. The term is used more generally to refer to the visual arts (such as painting, sculpture, ceramics, architecture, film and photography), rather than literature and music. Materials for use in the plastic arts, in the narrower definition, include those that can be carved or shaped, such as stone or wood, concrete, glass, or metal. History The word ''plastic'' draws from the Ancient Greek (''plastikós''), which means 'to mold' or 'to shape'. It has long preceded its dominant modern meaning as a synthetic material. The term ''plastic arts'' has been used historically to denote visual art forms (painting, sculpture, and ceramics) as opposed to literature or music. The related terms ''plasticity'' and ''plasticism'' became more widely used in the early 20th century by cri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cabaret Voltaire (band)
Cabaret Voltaire are an English music group formed in Sheffield in 1973 and initially composed of Stephen Mallinder, Richard H. Kirk, and Chris Watson (musician), Chris Watson. Named for Cabaret Voltaire (Zürich), the Zürich nightclub that fostered the early Dada movement, the band are often characterized as among the most innovative and influential Electronic music, electronic acts of their era. The band's early work consisted of experimentation with Do it yourself, DIY electronics and tape recorders, as well as Dada-influenced performance art, helping to pioneer industrial music in the mid-1970s. Finding an audience during the post-punk era, they gradually incorporated more conventional elements of synthpop, Dance music, dance, house music, house and funk music, funk styles. After Watson's departure in 1981, the group continued as a two-piece until disbanding in 1994. Kirk revived the name as a solo project from 2009 until his death in 2021. Watson and Mallinder announced o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hard Wired
''Hard Wired'' is the eighth full-length studio album by Canadian electro-industrial band Front Line Assembly, released in 1995. Production and themes The album was produced during the course of roughly five months. Singer Bill Leeb wrote the lyrics after the music was completed. The usual procedure for the band, as Leeb explained: "We write ..the music and then once we've got it finished, then I sit at home and start on the lyrics. I can't imagine writing any other way. ..I think with our music it's usually the sounds that inspire us." Lyrics-wise, the album addresses topics such as materialism and environmental issues, with an emphasis on the influence of technology: "I think most of the lyrics are basically about man versus technology. Basically, we’re destroying our planet with technology. At the same time, technology is the only thing that can save us. It's this constant struggle between these two forces that is making us go in whatever direction we're all going." Rel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armchair Apocrypha
''Armchair Apocrypha'' is the fourth solo studio album by the American singer-songwriter Andrew Bird. It was released on March 20, 2007, through Fat Possum Records. The album features more electric guitars, a change from the more acoustic-oriented album '' Andrew Bird & the Mysterious Production of Eggs'', though the songs are similar in character if slightly more straightforward. Writing and composition * "Simple X" is sampled from the song "Simple Exercises" by collaborator Dosh, off his solo album, Pure Trash. Lyrics, additional instrumentation and structure are provided by Bird. * An earlier version of "Imitosis," called "I" (also called "Capital I" live) appears on his 2003 album '' Weather Systems''. * The song "Darkmatter" contains similar lyrics as the song "Sweetbreads", which can be found on the live EP '' Fingerlings 1''. * Both bonus tracks also evolved from previous songs: "Sick of Elephants" was originally known as "Sycophantitis" and "Self-Torture" adds lyrics an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasticity (software) ...
Plasticity is a 3D computer graphics software program that runs on Windows, MacOS, and Linux. It runs on Parasolid's geometric modeling kernel. It is pitched as CAD for artists. Features * Non-uniform rational B-spline * Solid modeling * Polygon mesh modeling * Boolean operations * Real-time rendering * SpaceMouse support * Blender Bridge - Real-time sync between Plasticity and Blender File formats Import Export See also * List of 3D computer graphics software * List of 3D modeling software References {{Reflist External links nkallen/plasticity Computer-aided design Splines (mathematics) 3D computer graphics 3D graphics software Software Software consists of computer programs that instruct the Execution (computing), execution of a computer. Software also includes design documents and specifications. The history of software is closely tied to the development of digital comput ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasticity Forum
Ocean Recovery Alliance (ORA) is a 501c3 registered non-profit organization in California, and registered charitable organization in Hong Kong, with the aim to use new technologies, innovations, creativity and collaborations to solve issues that face the health of the ocean today. Foundation Ocean Recovery Alliance was founded by Douglas Woodring and Ashley Day in 2010. Doug, currently Managing Director of Ocean Recovery Alliance, also co-founded Project Kaisei in 2009, which led a science expedition to the North Pacific Gyre with Scripps Institution of Oceanography. The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) listed plastic pollution in the ocean as the first of three main focal points in their 2011 UNEP Yearbook, indicating the necessity of addressing how we use and dispose of plastics. One of the causes of plastic pollution is that so many of our disposable, single-use products, are made with a permanent material - plastic. With the growth of our "disposable" lifestyles ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |